HERMES
- heal health
- Jul 10, 2025
- 7 min read
Updated: Jul 18, 2025

In mythological realm, Hermes acted as a messenger between the gods and humans, facilitating the transfer of information and guiding souls. In biological realm, hormones, coming from the Greek word hormao, which means "to set in motion" or "to stir up”, are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream to regulate various processes in the body, much like how Hermes delivered messages. They convey signals between organs, tissues, and cells, facilitating communication within the body.
As the endocrine system is one of the two regulatory systems in the human body besides the nervous system, HERMES is inaugurated by Heal Health to dive deep into the roles of hormones in body stability.
Melatonin
Catch flights, not feelings.

The catchy phrase emphasises travel and adventure over emotional attachments. Yet, after a long distance flight, you are inevitably cursed with an infamous enemy - jet lag.
Our circadian rhythms are controlled by the hormone melatonin. When we fly to a different time zone, all the clocks in our body desynchronise. Each clock then takes a slightly different amount of time to re-adjust, which is why we feel so bad.
Melatonin production is regulated by the light-dark cycle, with light exposure suppressing its synthesis via retinal signals sent to the suprachiasmatic nucleus and then to the pineal gland. Besides sleep enhancement, it has potential role in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, adjunct therapy for anxiety disorders, menstrual cycle regulation and anti-cancer properties due to its role in apoptosis and tumor suppression.
Adrenaline

Is stress ever desirable? On one hand, it seems to create burn-out while enhancing productivity on the other hand. The culprit behind this is adrenaline, or epinephrine, released by the adrenal gland. As a central nervous system neurotransmitter, it’s a chemical messenger that helps transmit nerve signals across nerve endings to another nerve cell, muscle cell or gland cell.
During the fight-or-flight response, the brain perceives danger. Next, the hypothalamus sends a signal down your spinal cord, then out to your body. The neurotransmitter noradrenaline also reaches your adrenal gland, which releases the hormones adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine). These hormones travel through your blood to all parts of your body. They reach your eyes, heart, airways, blood vessels in your skin and your adrenal gland again. The “message” to these organs and tissues is to continue to react until you’re out of danger.
Synthetic epinephrine is used to treat CPR by stimulating your heart, eye surgery by keeping your pupils dilated, septic shock by increasing your blood pressure, asthma by opening airways and decreasing airway spasms and anaphylaxis by airway muscles.
Overall, high adrenaline is not a good indication of your health. Next time if you are in a stressful situation, give a laugh and save the day!
Histamine

Ever have an allergic reaction when exposed to timothy grass? If yes, you are probably the victim of histamine whose release peaks at cell reactivity. When the body detects an allergen, the immune system activates IgE antibodies, which bind to mast cells and basophils and cause degranulation, releasing histamine into the surrounding. Binding to H1 receptors causes vasodilation, vascular permeability that allows immune cells to leak out and cause swelling and stimulation of nerve endings leading to itching and pain. It also binds to H2 Receptors to increase mucus secretion and contribute to airway narrowing.
Does it mean we should get rid of histamine? Don’t make haste. As a neurotransmitter, histamine binds to H3 receptors which are mainly involved in blood-brain barrier and therefore studying H3 receptor antagonist medications for potential use in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Beside regulating appetite through acid secretion by binding to H2 receptors and formation of certain blood cells by binding to H4 receptors, it also controls the sleep-wake cycle.
Do not fret about histamine oversecretion as antihistamines are here to help! They block histamine receptors (mostly H1 receptors), preventing histamine from binding and reducing inflammation and symptoms.
Why is histamine called the “allergic hormone”(answer in the comment)
Ghrelin

Ever having an insatiable appetite? Don’t be under the delusion that it is your own volition as it is because you are under the influence of the mechanism of hormone ghrelin. Ghrelin levels typically rise before a meal, when your stomach is empty. Then they decrease shortly after, when your stomach is full.
Ghrelin is a 28-amino-acid peptide predominantly secreted in the stomach. This hormone is produced in your stomach and secreted when your stomach is empty. It enters your bloodstream and affects a part of your brain called the hypothalamus, which helps regulate your hormones and appetite. On the contrary, hormone leptin counteracts by decreasing the appetite. Hence, ghrelin plays a role in the short-term control of appetite while leptin controls long-term weight control.
Besides, ghrelin signals part of your brain called the hypothalamus to increase appetite, promotes fat storage, stimulates your pituitary gland to release growth hormones, stimulates your digestive system to move food from your stomach through your small and large intestines, contributes to controlling insulin release and plays a role in protecting your cardiovascular health.
Oxytoxin
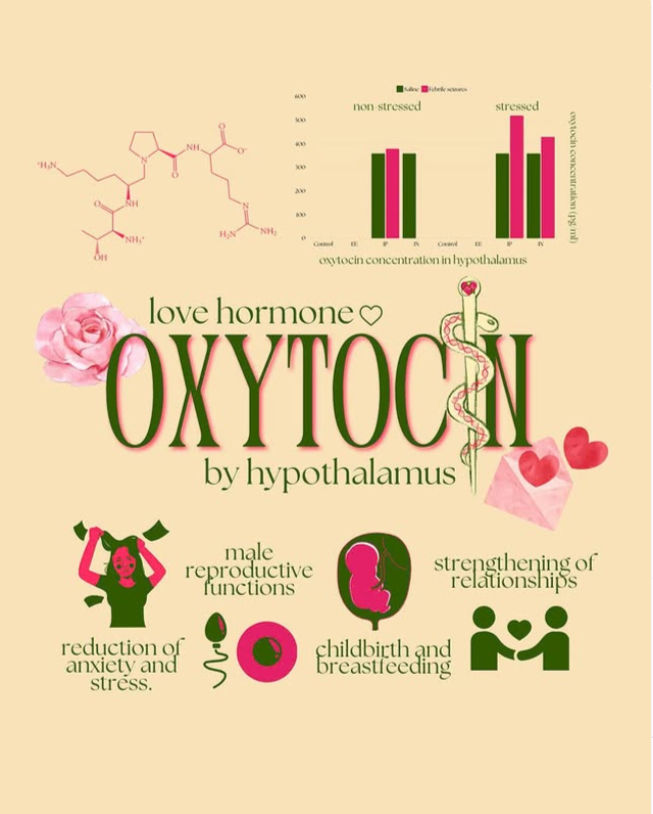
Have you ever received gifts on Valentine’s day? In theme of the annual White Day on 14 March, have you ever pondered if the sensation of love is purely psychological? Even animals like dogs experience love, when they get a big burst of it every time they make eye contact with their bonded humans. Behind the psychological impact lies the biological explanation of a peptide and neuropeptide Oxytocin. When a dog’s brain is flooded with the hormone, it’s better able to follow the social cues of its owners.
Produced in the hypothalamus and released into the bloodstream by the pituitary gland, Oxytocin both stimulates the muscles of the uterus to contract, and boosts the production of prostaglandins, which also increase uterine contractions. Women whose labor is slow to proceed are sometimes given oxytocin to speed the process. Once the baby is born, oxytocin helps to move milk from the ducts in the breast to the nipple, and to foster a bond between mom and baby.
To reinforce the role of the “love hormone” or “cuddle hormone”, oxytocin has an important role in many human behaviors and social interactions, including: sexual arousal, recognition, trust, romantic attachment and parent-infant bonding. Besides, oxytocin also reduces anxiety and stress as evident from the graph of higher oxytocin levels when stressed.
Dopamine

Ever having an unquenched thirst for boba or a craving appetite for junk food? What have these fast food and beverages companies done so well that drive customers in time after time despite the harmful health impacts? Customers are addictive to these products under the action of hormone Dopamine, a catecholamine that is released from the hypothalamus when humans are doing something pleasurable and want to seek more of that feeling.
Besides, dopamine is central critical for motor function via the nigrostriatal pathway whose loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain causes Parkinson’s disease. Imbalances are also linked to mood disorders like depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. It also controls lactation through inhibiting prolactin release, cardiovascular health, kidney and gastrointestinal motility.
Balance in dopamine is key to good health in humans. For now, it’s time to advocate for “dopamine detox”! The idea is to reset your brain and to make you enjoy healthy pleasures and not be tempted by addictive behaviours. You can’t really ‘detox’ from dopamine as it will always be in your brain, but the idea of being aware of your choices and habits can still help you to live the way you really want to.
Cortisol

What is your ideal work life? Having a fresh start in the morning and early dismissal in the afternoon? In today’s five-to-nine working environment, that is far from reality. For worse, you have seen doctors who burnout after working night shifts due to shortage of manpower. However, this alarmingly affects the pattern of cortisol release, which usually peaks in the morning and decreases in the evening.
As a glucocorticoid, cortisol is released by adrenal gland regulated by pituitary gland during stress. When the cortisol level in your blood falls, your hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing hormone. This directs your pituitary gland to make adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH then triggers your adrenal glands to make and release cortisol. Cortisol also regulates how your body uses glucose (sugar) for energy, decreases inflammation, regulates blood pressure and helps control your sleep-wake cycle.
To maintain a stable cortisol level, get quality sleep, practice deep breathing, enjoy and maintain healthy relationships!
Aldosterone

NaCl. This seemingly insignificant molecule actually has mighty power. In Medieval times, early civilizations used salt for trade, currency, and even as payment to soldiers, with the word “salary” originating from the Latin term “salarium,” referring to salt as payment. Now, salt is part and parcel to us, maintaining the electrolyte balance. Aldosterone is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal cortex, primarily responsible for regulating sodium and water balance in the body
When blood pressure falls, renin released by kidney splits angiotensinogen, a protein made by livers, into angiotensin I, which is inactive and hence split further into pieces by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) made from the lungs. One of those pieces is angiotensin II, an active hormone. Angiotensin II causes the muscular walls of small arteries (arterioles) to constrict, increasing blood pressure. Angiotensin II also triggers your adrenal glands to release aldosterone and your pituitary gland to release antidiuretic hormone (ADH, or vasopressin) that together cause kidneys to retain sodium. Aldosterone also causes kidneys to excrete potassium through urine. The increase in sodium in the bloodstream causes water retention. This increases blood volume and blood pressure, thus completing the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Thyroxine

Have you wonder why iodine, a trace mineral, is crucial? Thyroxine (T4) is a key hormone produced by the thyroid gland, composed of four iodine atoms and derived from the amino acid tyrosine. It circulates mostly bound to proteins and is converted in target tissues to its active form, triiodothyronine (T3). The hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis regulates thyroxine levels. The hypothalamus secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), stimulating the pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which in turn prompts the thyroid to produce T4 and T3.
Thyroxine plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development, especially in the brain during infancy. Deficiency in thyroxine causes hypothyroidism, leading to fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance, while excess causes hyperthyroidism, characterized by weight loss, heat intolerance, and anxiety. In infants, severe hypothyroidism can result in cretinism, causing developmental delays. Thyroxine replacement therapy is commonly used to treat hypothyroidism, highlighting its critical role in maintaining metabolic and physiological balance in the body.
Hence, adequate iodine intake, typically through iodized salt or iodine-rich foods (like seafood and dairy), ensures normal thyroxine production and healthy thyroid function.




Comments